There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|



| Index | ||
| S.No | Topic | |
| Daily Hindu Analysis | ||
| 1. | Where does India stand on acid attacks? | |
| 2. | Security camps, the game changer in the Maoist fight | |
| 3. | U.S. forces capture Maduro after strikes on Venezuela | |
| 4. | Venezuela crisis unlikely to hit India’s energy security | |
| 5. | Centre relaxes norms for start-ups to get funds from DSIR | |
| 6. | Gandhinagar typhoid surge: 100 hospitalised | |
| 7. | Army signs deal to procure long-range rocket launchers backed by Israeli technology | |
| 8. | India’s Russian oil imports at six-month high in November | |
| 9. | Earthlife is made of space stuff, studies of asteroid Bennu hint | |
| 10. | A winter getaway in Assam’s wetlands | |
|
| ||
| Daily Current Affairs | ||
| 11. | Karnataka sets record in organ donation in 2025 | |
| 12. | India’s first government hospital-based AI clinic inaugurated | |
| 13. | Delhi Police trace over 1,300 missing persons under Operation Milap | |
| 14. | Bulgaria joins eurozone | |

Context
The article examines India’s legal, social, and institutional response to acid attacks, using the prolonged legal battle of survivor and activist Shaheen Malik to highlight gaps in justice delivery, under-reporting of crimes, and low conviction rates despite stringent laws.
Detailed Analysis
Understanding Acid Attacks
Scale and Trends in India
Causes and Social Context
Legal Framework in India
Implementation Gaps
Case of Shaheen Malik
Suggestions Highlighted by the Author
UPSC Mains Question
Despite stringent laws, acid attacks continue to be under-reported and under-convicted in India. Examine the reasons and suggest measures to ensure effective prevention and survivor-centric justice.

Context
The article analyses India’s recent success in curbing Left Wing Extremism (LWE), arguing that the establishment of security camps in remote Maoist-dominated areas, especially in Bastar, has been the decisive factor in reversing insurgent control and restoring state authority.
Detailed Analysis
Decline of Maoist Violence
Why Maoism Flourished Earlier
Security Camps as a Turning Point
Psychological and Intelligence Impact
Developmental Spillovers
Shrinking Maoist Capacity
Suggestions by the Author
Move Beyond Security-Centric Approach
Strengthen Tribal Self-Governance
Integrated Long-Term Vision
UPSC Mains Question
“Security camps have played a decisive role in weakening Left Wing Extremism in India, but security measures alone cannot ensure lasting peace.” Critically examine.

Context
The United States carried out a large-scale military operation against Venezuela, capturing President Nicolás Maduro after air and naval strikes, triggering a major geopolitical crisis in Latin America.
Key Points
U.S. Military Action
Charges by the United States
Reasons Cited by the U.S.
Venezuela’s Response
Geopolitical Implications
Venezuela
Source: The Hindu
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding Venezuela:
1. Venezuela possesses the world’s largest proven oil reserves.
2. Angel Falls, the world’s highest waterfall, is located in the Andes Mountains of Venezuela.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. Venezuela has the world’s largest proven oil reserves.
Statement 2 is incorrect. Angel Falls is located in the Guiana Highlands, not the Andes Mountains.
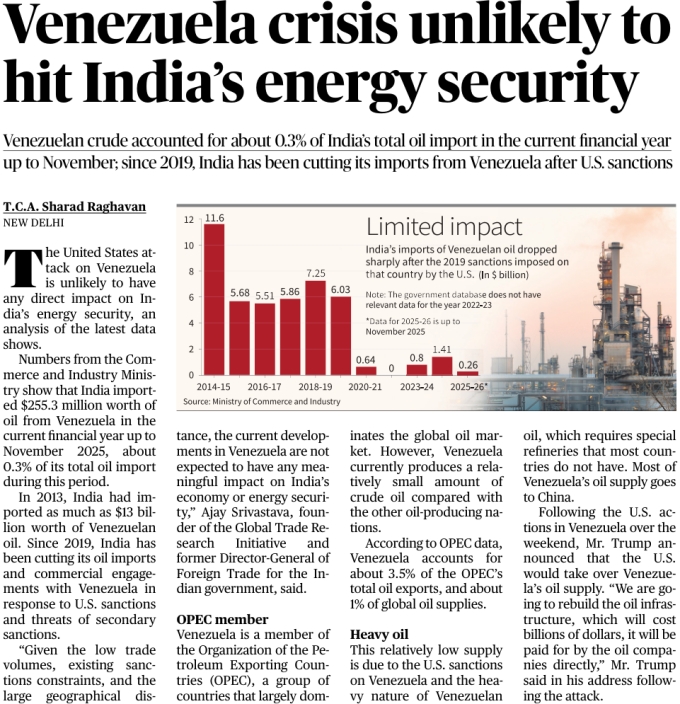
Context
Renewed geopolitical tensions involving Venezuela and the United States raised concerns over global oil supplies. However, recent data shows that India’s energy security remains largely insulated due to its minimal dependence on Venezuelan crude.
Key Points
Minimal Share in India’s Oil Basket
Sharp Decline Since 2019
Long-Term Import Trend
Nature of Venezuelan Crude
Limited Global Supply Role
India’s Energy Strategy
Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Venezuelan crude currently accounts for less than 1% of India’s total oil imports.
2. India has increased its oil imports from Venezuela after 2019 due to discounted heavy crude.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:

Context
The Union Government has relaxed eligibility norms for deep-tech start-ups to access financial assistance from the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (DSIR), aiming to accelerate innovation and early-stage scaling.
Key Points
Policy Decision
Financial Assistance
Objective of the Move
Quality and Evaluation Safeguards
Announcement Platform
Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (DSIR)
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements:
1. DSIR functions under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
2. Under the Industrial Research and Development Promotion Programme, DSIR provides financial assistance only to start-ups that have completed at least three years of operation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct as DSIR is under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
Statement 2 is incorrect because the three-year existence criterion has been removed for deep-tech start-ups.

Context
A surge of suspected typhoid cases in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, has led to the hospitalisation of over 100 people, prompting emergency public health measures amid reports of unsafe water supply.
Key Points
Current Situation
Administrative Response
Water Safety Concerns
High-Level Monitoring
Typhoid Fever
About
Transmission and Risk
Symptoms
Disease Burden
Treatment Challenges
Prevention
Gavi – The Vaccine Alliance
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Typhoid fever is caused by a virus and spreads through airborne transmission.
2. WHO recommends the use of typhoid conjugate vaccines in routine immunisation programmes in endemic countries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Army signs deal to procure long-range rocket launchers backed by Israeli technology
Context
The Indian Army has signed a contract under emergency procurement powers to acquire an advanced long-range rocket launcher system, aimed at significantly enhancing its deep-strike artillery capability.
Key Points
Contract Details
· Indian Army signed a ₹293 crore contract with NIBE Ltd., a private Indian defence manufacturer.
· Procurement carried out under Emergency Procurement (EP) provisions.
Technology Collaboration
· The system is being developed in collaboration with Israel, under a Technology Collaboration Agreement with Elbit Systems.
· Manufacturing will take place in India, marking a boost to Make in India in defence.
About the Rocket Launcher System
· Name: Suryastra Universal Multi-Calibre Rocket Launcher System.
· Strike range: 150 km to 300 km.
· Accuracy: Circular Error Probable (CEP) of less than 5 metres.
· Capable of precision surface-to-surface strikes.
Operational Capabilities
· Can integrate multiple rocket types on a single platform.
· Designed to engage multiple targets simultaneously at varying ranges.
· Enhances operational reach, firepower, and responsiveness of artillery units.
Strategic Significance
· First time a high-precision rocket launcher with up to 300 km range is being produced domestically.
· Strengthens India’s deep-strike deterrence and indigenous defence ecosystem.
Emergency Procurement (EP) Provisions
· Cleared by the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC).
· Allows armed forces to procure weapons up to ₹300 crore per contract on an urgent basis.
· Aimed at fast-tracking capability enhancement without lengthy approvals.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements:
1.The Suryastra rocket launcher system has a strike capability of up to 300 km and is being manufactured in India.
2.Emergency Procurement provisions allow defence acquisitions only after Cabinet Committee on Security approval.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Suryastra is a domestically produced system with a strike range of up to 300 km.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Emergency Procurement provisions allow urgent procurement without further clearances, including CCS approval.
Context
India’s imports of Russian crude oil rose to a six-month high in November 2025, increasing Russia’s share in India’s overall oil imports amid ongoing diversification of energy sources.
Key Points
Rising Russian Oil Imports
· India imported 7.7 million tonnes of Russian oil in November 2025.
· This accounted for about 35% of India’s total crude oil imports for the month.
· Imports were the highest since May 2025, both in volume and value terms.
Value of Imports
· In value terms, India imported $3.7 billion worth of Russian crude in November 2025.
· Russian oil constituted nearly 34% of India’s total oil import bill that month.
Energy Diversification Strategy
· Alongside Russia, India increased crude purchases from the United States, which touched a seven-month high, contributing nearly 13% of total imports.
· Together, Russia and the U.S. supplied nearly half of India’s oil imports in November.
Geopolitical and Trade Context
· The surge occurred amid slow progress in finalising a trade deal with the U.S.
· Discounted Russian crude continues to remain attractive for India’s refiners.
· The approach reflects India’s pragmatic energy security strategy amid global volatility.
Implications for India
· Helps contain domestic fuel prices by leveraging discounted crude.
· Reduces over-dependence on traditional West Asian suppliers.
· Strengthens India’s negotiating position in global energy markets.
Ministry of Commerce and Industry
· The import data has been compiled and released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
· It tracks both volume and value of crude oil imports to assess trade and energy trends.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding India’s crude oil imports:
1.In November 2025, Russia accounted for more than one-third of India’s total crude oil imports.
2.The United States and Russia together supplied less than one-fourth of India’s crude oil imports in November 2025.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Russia’s share was about 35% of India’s total crude oil imports.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Russia and the U.S. together supplied nearly half, not less than one-fourth, of India’s crude oil imports.
Context
Recent studies based on samples brought back from asteroid Bennu by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission suggest that key molecular ingredients required for life on Earth may have originated in space and were delivered through asteroids.
Key Points
OSIRIS-REx Mission Findings
· Samples collected from asteroid Bennu contain ribose, glucose, amino acids, nucleobases, and nitrogen-rich polymers.
· These molecules are essential building blocks for RNA and DNA, strengthening theories on the cosmic origin of life’s ingredients.
Support for the RNA World Hypothesis
· The presence of ribose and nucleobases supports the idea that RNA may have preceded DNA as the first genetic material.
· Asteroids could have delivered these molecules to early Earth over 3.5 billion years ago.
Chemical Complexity of Bennu
· Scientists detected pre-solar grains originating from supernovae, indicating material older than the Sun.
· Bennu shows evidence of chemical reactions in icy environments, producing complex organic polymers before the formation of planets.
Role of Asteroids in Early Earth
· During early solar system formation, asteroids like Bennu likely transported organic compounds, water, and nitrogen to Earth.
· This could have enabled chemical reactions near hydrothermal vents, aiding the emergence of life.
Significance for Planetary Science
· Findings provide insights into planet formation, distribution of organic matter, and conditions that make life possible.
· Raises questions on whether similar processes occurred on other planets, increasing prospects of life beyond Earth.
· OSIRIS-REx stands for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security–Regolith Explorer.
· It collected samples from Bennu in 2020 and returned them to Earth in 2023, marking the first U.S. asteroid sample-return mission.
· Objective: Study the origin of the solar system and life, and assess asteroid impact risks.
Source: The Hindu
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding asteroid Bennu and the OSIRIS-REx mission:
1. Samples from asteroid Bennu contain organic molecules such as amino acids and nucleobases.
2. The findings support the theory that all life on Earth originated exclusively on the planet itself.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct as Bennu samples contain key organic molecules. Statement 2 is incorrect because the findings suggest that ingredients of life may have been delivered from space, not that life originated exclusively on Earth.

Context
Assam’s wetlands and Ramsar sites have witnessed a fresh influx of migratory birds during the winter season, highlighting the State’s importance as a key wintering habitat and boosting biodiversity and eco-tourism.
Key Points
Seasonal Migration to Assam
· Migratory birds arrive annually to escape the harsh winters of Siberia, Central Asia, Tibet and Europe.
· Assam’s wetlands provide warmer climate, abundant food and safe roosting grounds.
Major Migratory Species Observed
· Bar-headed geese, northern pintails, ruddy shelducks, falcated ducks, ferruginous pochards, and glossy ibises.
· These species are known for long-distance and high-altitude migrations.
Important Wetlands and Birding Sites
· Prominent sites include Deepor Beel (Ramsar site) near Guwahati, Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, Kaziranga National Park wetlands, Maguri Motapung Beel, Panidihing Beel, and Son Beel.
· These wetlands act as critical wintering and staging grounds.
Ecological Significance
· Migratory birds enhance wetland nutrient cycles and ecological balance.
· Their presence reflects the ecological health of wetland ecosystems.
Eco-tourism and Local Livelihoods
· Seasonal bird influx supports birdwatching tourism and local economies.
· Conservation-linked tourism promotes community awareness and habitat protection.
Threats and Conservation Concerns
· Unsustainable development, encroachment, pollution and habitat degradation pose risks.
· Continued protection of wetlands is vital for sustaining migratory routes.
Ramsar Convention
· The Ramsar Convention is an international treaty for wetland conservation and wise use.
· Assam hosts multiple Ramsar sites, reinforcing India’s commitment to wetland biodiversity.
Source: The Hindu
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Q. Consider the following statements regarding Assam’s wetlands:
1.Assam’s wetlands serve as important wintering habitats for migratory birds from Central Asia and Europe.
2.Deepor Beel is a Ramsar site that supports migratory bird populations during winter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Both statements are correct. Assam’s wetlands attract migratory birds from colder regions, and Deepor Beel is a designated Ramsar site known for supporting migratory avifauna.
Syllabus: GS 2 – Health | Governance | Social Justice
Context
Karnataka has achieved its highest-ever annual organ donation tally in 2025, reflecting improved public awareness, institutional coordination and effective implementation of the organ transplantation framework.
Key Points
Record Achievement
National Ranking
Role of Jeevasarthakathe
Donor Profile
Significance
Additional Information: Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Karnataka ranked third among Indian States in organ donation in 2025.
2. The Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994 allows commercial organ donation under regulated conditions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct as Karnataka ranked third nationally in organ donation in 2025.
Statement 2 is incorrect because the Act strictly prohibits commercial and illegal organ trade.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS 2 – Health | GS 3 – Science and Technology
Context
India inaugurated its first government hospital-based Artificial Intelligence (AI) clinic at the Government Institute of Medical Sciences (GIMS), marking a significant step towards technology-driven public healthcare delivery.
Key Points
Inauguration and Framework
Nature of the AI Clinic
Objectives
Significance
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding India’s first government hospital-based AI clinic:
1. It has been established at the Government Institute of Medical Sciences under a centre for medical innovation.
2. Its primary objective is to allow AI-based healthcare solutions to be tested and validated in real clinical settings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2
Explanation:
The AI clinic is located at GIMS under the Centre for Medical Innovation and is designed to provide a real-world clinical environment for developing and validating AI healthcare solutions.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS 2 – Governance | Internal Security | Police Reforms
Context
Delhi Police traced 1,303 missing persons in the southwest district over the past year under Operation Milap, reflecting sustained efforts to reunite families and enhance public trust in policing.
Key Points
About Operation Milap
Overall Achievements (Past Year)
Operational Strategy
Role of Public Outreach
Significance
Q. Operation Milap is associated with which of the following?
(a) Tracing missing persons
(b) Counter-terrorism operations
(c) Cybercrime investigation
(d) Disaster relief operations
Correct Answer: (a) Tracing missing persons
Explanation:
Operation Milap is a Delhi Police initiative aimed at tracing missing persons, particularly children and vulnerable adults, and reuniting them with their families.
Syllabus: GS 1 – Geography (Mapping) | GS 2 – International Relations (Europe)
Context
Bulgaria officially adopted the euro on January 1, 2026, becoming the 21st member of the eurozone and retiring its national currency, the Bulgarian lev, after meeting EU convergence criteria.
Key Points
About Bulgaria
Location and Borders
Major Geographical Features
About the Eurozone
Evolution
Members
Key Features
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements:
1. Bulgaria is located in the Balkan Peninsula and has a coastline along the Black Sea.
2. With Bulgaria’s entry, the eurozone consists of 21 member countries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Bulgaria lies in the Balkan Peninsula with a Black Sea coastline, and its adoption of the euro in 2026 makes it the 21st eurozone member.
Source: Indian Express