There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|



| Index | ||
| S.No | Topic | |
| Daily Hindu Analysis (YouTube) | ||
| 1. | Budget 2026-27 must keep the growth momentum | |
| 2. | Expert panel sets norms for religious sites in sanctuaries | |
| 3. | Union govt. sets goal to formally recognise one lakh tribal healers as ‘partners in health services’ | |
| 4. | ISMA suggests measures for the promotion of biofuel | |
| 5. | Secretary-General of RS has administrative role only, says court | |
| 6. | India-EU free trade pact will be ‘mother of all deals’: Goyal | |
| 7. | Highest annual spike saw 44,000 start-ups added last year: Modi | |
| Daily Current Affairs (App) | ||
| 8. | Gharial | |
| 9. | Export Preparedness Index 2024 | |
| 10. | NPS Vatsalya Scheme | |
| 11. | Vultures in India | |
| 12. | Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana–National Rural Livelihoods Mission: National Campaign on Entrepreneurship | |
| 13. | Responsible Nations Index: A New Global Initiative | |

Context
The article discusses how Budget 2026–27 should sustain India’s growth momentum amid global uncertainties. It argues that India’s economic resilience in 2025 was driven by reforms and policy continuity, and that the upcoming Budget must strengthen domestic growth drivers while maintaining fiscal discipline. The author outlines sector-wise priorities and structural reforms needed to crowd in private investment and enhance competitiveness.
Detailed Analysis
1. Strengthening Domestic Growth Levers· The author emphasises prioritising productive capital expenditure and social sector spending to boost demand and long-term growth. This should be done while adhering to the fiscal consolidation glide path to keep debt risks under control.
2. Continued Focus on Defence· Increase defence capital outlay to 30% (from ~26.4%).· Enhance funding for DRDO by at least ₹10,000 crore.· Expand defence industrial corridors (currently in UP and Tamil Nadu) and consider establishing one in eastern India.· Promote defence exports through a dedicated export promotion council to meet the target of ₹50,000 crore by 2028–29.Example: Private enterprises already contribute nearly 65% of defence exports, showing the scope for further expansion.
3. Clean Energy and Critical Minerals· The transition to clean energy and strategic technologies is driving demand for critical minerals.· The National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) provides a strategic base, which should be supported by:o A dedicated tailings recovery programme Specialised financing mechanisms for critical minerals
4. Export Competitiveness· Exports need a strong policy push in a challenging global environment.· The allocation for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) at around ₹18,233 crore should be enhanced to improve export competitiveness.
5. Global Capability Centres (GCCs) and Tax Clarity· India has emerged as a global hub for Global Capability Centres.· However, ambiguity in transfer pricing (TP) norms remains.· Clear TP guidelines for different GCC categories can improve investor confidence.
6. Drone Ecosystem and Emerging Technologies· To accelerate drone adoption and exports:· Enhance PLI outlay from ₹120 crore to ₹1,000 crore· Establish a ₹1,000 crore Drone R&D FundThis would support innovation, exports, and global competitiveness.
7. Deepening Corporate Bond Markets· Diversifying finance beyond banks is critical.· Suggested measures include:· Lowering qualifying borrowing thresholds· Including unlisted corporates· Increasing insurance investment caps beyond 25%· Revising “Approved Investment” norms from AA to A-
These steps can channel capital to high-quality but lower-rated issuers. 8. Addressing Tax Disputes· Pendency at the CIT(A) level is a major bottleneck.· The article suggests:· Prioritising high-value and time-sensitive cases· Adopting a dual-track disposal system (fast-track + detailed track)· Filling nearly 40% vacancies at the appellate level 9. Trade Facilitation and Customs Reforms· Remove restrictions that exclude newly incorporated companies from AEO certification.· Continue customs tariff rationalisation to:o Reduce inverted duty structureso Improve manufacturing competitiveness
Suggestions of the Author·
Maintain fiscal prudence while increasing growth-oriented capex· Strengthen defence, exports, clean energy, and emerging technologies· Provide policy certainty in taxation and trade· Resolve structural bottlenecks in finance and dispute resolution
UPSC Mains Question
How can Budget 2026–27 balance fiscal consolidation with the need to sustain growth momentum in the Ind

Context
An apex expert body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has issued guidelines on permitting religious structures inside wildlife sanctuaries, following concerns over land diversion and unresolved forest rights claims. Key PointsBackground of the Issue· The issue arose from a proposal related to Balaram Ambaji Wildlife Sanctuary, Gujarat, involving diversion of forest land for religious use.· It highlighted unresolved forest rights and the risk of setting precedents for similar demands in protected areas. Expert Panel and Its Role· The guidelines were framed by an expert body under the Ministry that advises on infrastructure development within wildlife habitats.· The aim is to regulate construction and expansion of religious sites inside protected areas. Core Guidelines· Any construction or expansion on forest land after 1980 should generally be treated as encroachment.· Religious structures inside sanctuaries cannot claim automatic legitimacy based on faith or historical presence.· Forest rights must be formally recognised and recorded before any consideration of land use.
Exceptional Provision· In rare cases, if a State government issues a reasoned and documented order, proposals for regularisation may be referred to the Ministry.· Such cases will be examined strictly on a case-by-case basis. Concerns Raised During Deliberations· Several sanctuaries across India have pending forest rights claims.· Allowing land diversion without settlement of rights could weaken wildlife protection frameworks.· Risk of religious use becoming a route for regularising encroachments in protected areas. Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife· It is an independent body under the National Board for Wildlife.· Comprises not more than 10 members of the NBWL.· Chaired by the Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change. Functions as a project clearance body, regulating land diversion within:o Protected Areaso Eco-Sensitive Zones
Difference from NBWL· Standing Committee:
Deals with project-level approvals and land diversion cases.· National Board for Wildlife: Handles policy-level decisions related to wildlife conservation. UPSC Prelims Practice QuestionQ. Consider the following statements regarding the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SCNBWL):1.It is chaired by the Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.2.It deals primarily with policy-level decisions on wildlife conservation.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(a) 1 only(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2Correct Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:Statement 1 is correct as the Environment Minister chairs the Standing Committee.Statement 2 is incorrect because policy-level decisions are handled by the National Board for Wildlife, not its Standing Committee.

Context
The Union government announced its plan to formally recognise one lakh tribal healers as partners in health services at a capacity-building event organised by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, highlighting efforts to strengthen healthcare delivery in tribal areas.
Key PointsObjective of the Initiative·
To formally recognise tribal healers as partners in strengthening health services for tribal communities.· To integrate traditional medicine and local health practices with the formal public health system. Capacity Building and Skill Enhancement· Sessions to be conducted by experts from AIIMS, WHO, ICMR, Health Ministry, and AYUSH Ministry.· Focus on enhancing:o Technical knowledge Service delivery capacitieso Disease surveillance and referral practices
Role of State Governments·
States urged to explore market linkages and partnerships with:· FMCG companies· Pharmaceutical companies· Aim is to generate livelihood opportunities for tribal healers in the traditional medicine sector.
MoU and Institutional Support·
Ministry of Tribal Affairs signed an MoU with ICMR–Regional Medical Research Centre, Bhubaneswar.· Objective is to establish the first national tribal health observatory. Bharat Tribal Health Observatory· The observatory will:o Institutionalise tribe-disaggregated health surveillanceo Support implementation researcho Promote research-driven disease elimination· Special focus on diseases such as:o Malariao Leprosyo Tuberculosis· Addresses long-standing gaps in tribal-specific health data and evidence-based planning. Participation· Over 400 tribal healers from Scheduled Tribe communities across India attended the event.
Ministry of Tribal Affairs·
Nodal ministry for tribal welfare, development, and empowerment.· Plays a key role in integrating tribal knowledge systems with mainstream development initiatives.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the Bharat Tribal Health Observatory:
1.It aims to promote tribe-disaggregated health data and research-driven disease elimination in tribal areas.2.It is being set up under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(a) 1 only(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2Correct Answer:
(a) 1 onlyExplanation:Statement 1 is correct as the observatory focuses on tribal-specific health surveillance and research.Statement 2 is incorrect because it is being set up through the Ministry of Tribal Affairs in collaboration with ICMR. Source: The Hindu

Context
The Indian Sugar and Bio-energy Manufacturers Association urged the Union government to undertake GST rationalisation and targeted policy support to promote biofuels and strengthen the clean mobility ecosystem.
Key PointsDemand for GST Rationalisation·
Rationalise GST on flex-fuel vehicles and hybrids, placing them alongside EVs as mainstream clean mobility solutions.· Bring ethanol-related machinery under 5% GST to reduce production costs and encourage investment. Support for Advanced Biofuels· Incentivise advanced biofuels, including:o Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)o Green hydrogeno Isobutanol· These fuels can help diversify India’s energy mix and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Sugar Sector as a Bio-energy Hub· The sugar sector can evolve into a multi-vertical bio-energy hub.· Biofuels provide additional revenue streams for sugar mills and improve farmer incomes through better utilisation of agricultural produce. Clean Mobility and Energy Security· Biofuels complement EVs in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.· Promote domestic fuel production to address rising crude oil prices and enhance energy security. Biofuels· Biofuels are hydrocarbon fuels derived from organic matter in a short time span.· Forms:· Solid: wood, dried plant material, manure· Liquid: bioethanol, biodiesel· Gaseous: biogas· Used in transport, electricity generation, and heating. Categories of Biofuels·
First Generation: Made from food crops like sugar and starch; easy to produce but affect food security.·
Second Generation: Produced from non-food biomass and waste; lower emissions but technologically complex.·
Third Generation: Derived from algae and micro-organisms; reduce pressure on land and water resources.·
Fourth Generation: Use genetically engineered crops with carbon capture and storage; potentially carbon negative. Indian Sugar and Bio-energy Manufacturers Association· Apex industry body representing the sugar and bio-energy sector.· Advocates policy reforms to promote ethanol blending, biofuels, and clean energy transition.
UPSC Prelims Practice QuestionQ. Consider the following statements regarding biofuels:
1.Second-generation biofuels are produced from non-food biomass and generally emit fewer greenhouse gases than first-generation biofuels.
2.Fourth-generation biofuels involve carbon capture and geo-sequestration and may be carbon negative.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(a) 1 only(b) 2 only(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2Correct Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2
Explanation:Second-generation biofuels use agricultural waste and non-food biomass with lower emissions.Fourth-generation biofuels combine biofuel production with carbon capture, making them potentially carbon negative. Source: The Hindu

Context
The Supreme Court clarified that the Secretary-General of the Rajya Sabha has only an administrative role and should not assume quasi-judicial functions, while examining a case related to the admissibility of a notice for removal of a High Court judge.
Key PointsSupreme Court’s Observation·
A Bench of Justices Dipankar Datta and S.C. Sharma held that the Secretary-General of the Rajya Sabha has a purely administrative role.· The Court stated that preparing a “draft decision” on the admissibility of a motion goes beyond administrative authority.
Issue Before the Court·
The Secretary-General had prepared a draft concluding that the MPs’ notice for removal of a judge was not admissible.· The Rajya Sabha Deputy Chairman relied on this draft to reject the notice.
Limits of Authority· The Court emphasised that the Secretary-General should exercise restraint.· Decisions on admissibility of motions must be left to:· The Speaker of the Lok Sabha, or· The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, as applicable. Concerns Highlighted· The draft decision stated that MPs did not use proper terms, failed to provide authenticated documents, and cited an incorrect legal provision.· The Court warned against the Secretariat assuming a quasi-adjudicatory role. Broader Constitutional Principle· Parliamentary secretariats are meant to assist presiding officers, not replace their constitutional discretion.· Any deviation may affect the separation between administrative support and constitutional decision-making. Rajya Sabha Secretariat· The Secretary-General is the administrative head of the Rajya Sabha Secretariat.· Appointed by the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha (Vice President of India).· Ranks equivalent to the Cabinet Secretary in the Indian order of precedence.· Exercises administrative and financial powers on behalf of the Chairman, including:· Determining staff strength· Recruitment rules· Initiating budget proposals· Does not possess quasi-judicial or decision-making powers on parliamentary motions.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the Secretary-General of the Rajya Sabha:
1.The Secretary-General is appointed by the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.2.The Secretary-General has the authority to decide on the admissibility of motions submitted by Members of Parliament.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(a) 1 only(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
The Union Commerce Minister stated that the proposed free trade agreement between India and the European Union would be the most significant deal signed by India so far, highlighting its scale and economic impact.
Key PointsIndia–EU Free Trade Agreement· The proposed FTA with the European Union is described as the largest and most comprehensive trade deal for India.· It is expected to surpass the seven FTAs India has already signed with developed countries. Government’s Position· The statement was made by Piyush Goyal, Union Minister of Commerce and Industry.· The Minister described the deal as a win-win arrangement for both India and the EU. Comparison with Earlier FTAs· Since 2014, India has signed FTAs with:· United Kingdom· Mauritius· United Arab Emirates· Australia· EFTA countries (Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, Liechtenstein)· An early harvest deal has also been signed with Oman.· The India–EU FTA is expected to be more comprehensive than all these agreements. Sectoral Complementarity· India and the EU have different economic strengths, reducing direct competition.· Sectors of interest to India receive strong market access, while EU priorities are addressed separately, ensuring balance. Timeline and Negotiations· The Minister neither confirmed nor denied the January 27 deadline for concluding the deal.· Negotiations are ongoing, indicating complexity and depth of the agreement. Importance of the Deal· Enhances market access for Indian goods and services.· Strengthens India’s position in global value chains.· Reinforces India’s strategy of deepening trade ties with developed economies.
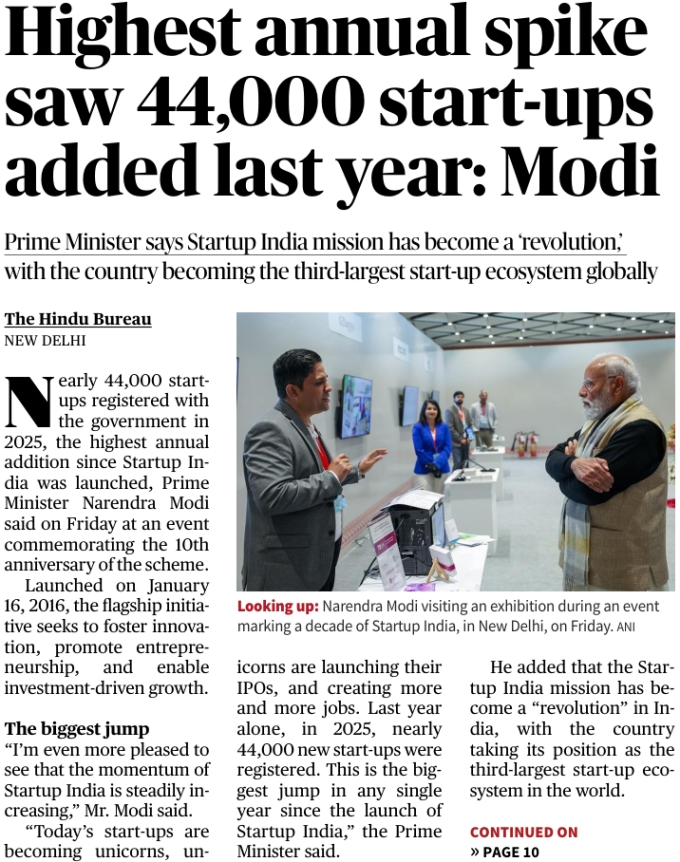
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted that nearly 44,000 start-ups were registered in 2025, marking the highest annual addition since the launch of the Startup India mission, while addressing an event commemorating its 10th anniversary. Key PointsRecord Growth in Start-ups· Nearly 44,000 new start-ups were added in 2025.· This is the highest annual spike since the inception of Startup India.· Reflects growing entrepreneurial momentum across sectors. Startup India Mission· Launched on January 16, 2016.· Aims to:· Foster innovation· Promote entrepreneurship· Enable investment-driven growth Global Standing of India· India has emerged as the third-largest start-up ecosystem in the world.· Growth driven by:· Rising number of unicorns· Increased IPOs by start-ups· Expansion of job creation Economic Impact· Start-ups are:· Creating large-scale employment· Supporting technology-driven solutions· Strengthening India’s position in the global innovation landscape Startup India· Flagship initiative of the Government of India.· Provides:· Regulatory support· Tax incentives· Funding and incubation ecosystem· Focuses on building a robust start-up and innovation culture. UPSC Prelims Practice QuestionQ. Consider the following statements regarding the Startup India initiative:1.Startup India was launched in 2016 to promote innovation and entrepreneurship.2.India currently ranks as the largest start-up ecosystem in the world.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(a) 1 only
(b) 2 onlySyllabus: GS 3: Environment and Ecology – Biodiversity and Conservation
Context:
A recent comprehensive survey across the Ganga River basin recorded 3,037 gharials in 13 rivers, highlighting both conservation gains and continuing threats to this critically endangered species.
Key Points
About Gharial
• A freshwater crocodilian belonging to the Order Crocodylia and Family Crocodylidae.
• Scientific name: Gavialis gangeticus.
• Name derived from Hindi word ghara, referring to the pot-shaped bulb on adult males’ snouts.
Distribution
• Historically found in rivers of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
• Present strongholds in Chambal and Girwa rivers (India) and Rapti–Narayani river (Nepal).
• Gharial reserves in Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Physical Features
• One of the largest crocodilians; males reach 5–6 m, females 3.5–4.5 m.
• Long, narrow snout adapted for fish-eating.
• Adult males possess a bulbous structure called ghara.
• Most aquatic crocodilian; rarely leaves water except for basking and nesting.
Ecology and Behaviour
• Primarily piscivorous, playing a key role in riverine ecosystems.
• Mating season: November–January.
• Egg-laying period: March–May, on sandy riverbanks.
Conservation Status
• Listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
• Threats include river pollution, sand mining, fishing nets, and habitat fragmentation.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Gharial:
1. It is the most aquatic among all crocodilian species.
2. Its major surviving populations are concentrated in the Ganga river system.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
• Statement 1 is correct: Gharials are highly aquatic and rarely move far from water.
• Statement 2 is correct: The main surviving populations are found in tributaries of the Ganga basin.
Source: NIE
Syllabus: GS 3: Economy – External Trade, Industrial Policy
Context:
NITI Aayog recently released the Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2024 to assess how well Indian States and Union Territories are positioned to boost exports and contribute to India’s global trade ambitions.
Key Points
What is Export Preparedness Index (EPI)
• A comprehensive tool to evaluate export readiness of States and UTs.
• Highlights subnational role in strengthening India’s export ecosystem.
Editions and Coverage
• First edition released in August 2020.
• EPI 2024 is the fourth edition.
Framework and Structure
• Based on 4 pillars, 13 sub-pillars and 70 indicators.
• Weightage distribution:
– Business Ecosystem – 40%
– Export Infrastructure – 20%
– Policy and Governance – 20%
– Export Performance – 20%
Classification of States and UTs
• Categorised into Large States, Small States, North Eastern States, and UTs.
• Performance grouped as Leaders, Challengers, and Aspirers.
Leading Performers – EPI 2024
• Large States: Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh.
• Small States / NE States / UTs: Uttarakhand, Jammu and Kashmir, Nagaland, Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Goa.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2024:
1. The Export Preparedness Index is released by NITI Aayog to assess export readiness of States and Union Territories.
2. In EPI 2024, Export Performance carries the highest weightage among all pillars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
• Statement 1 is correct: EPI is released by NITI Aayog to assess subnational export preparedness.
• Statement 2 is incorrect: The Business Ecosystem pillar has the highest weightage (40%), not Export Performance.
Source: PIB
Syllabus: GS 2: Governance, Polity, and International Relations – Government Policies and Interventions
Context:
The Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) recently issued guidelines for the NPS Vatsalya Scheme 2025, a contributory savings and long-term financial security scheme designed for minors in India.
Key Points
About NPS Vatsalya Scheme
• A scheme introduced for minors to provide long-term financial security.
• Exclusively targeted at minor Indian citizens, including NRIs and OCIs.
Eligibility
• Available for all Indian citizens, including NRIs/OCIs, under the age of 18 years.
• The account is opened in the minor’s name but operated by their guardian.
Contributions
• Minimum contribution of ₹250 initially and annually, with no upper limit on contributions.
• Contributions can be made by the minor, guardian, or even gifted by relatives and friends.
Pension Fund Selection
• The guardian selects any Pension Fund registered with PFRDA.
Partial Withdrawal Provisions
• Partial withdrawal allowed after 3 years from account opening.
• Up to 25% of own contributions (excluding returns) can be withdrawn for:
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding the NPS Vatsalya Scheme:
1. The scheme is open to Indian citizens, NRIs, and OCIs under the age of 18.
2. The guardian is not allowed to choose a pension fund for the minor.
3. Partial withdrawal is allowed after 3 years for education, medical treatment, and disabilities.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
• Statement 1 is correct: The scheme is available for Indian citizens, NRIs, and OCIs under 18 years.
• Statement 2 is incorrect: The guardian is allowed to select a pension fund.
• Statement 3 is correct: Partial withdrawals are allowed for specified purposes like education and medical treatment after 3 years.
Source: PIB
Syllabus: GS 3: Environment, Ecology, Biodiversity, and Climate Change – Conservation, Environmental Pollution, and Degradation
Context:
Tamil Nadu has informed the Madras High Court about the creation of Vulture Safe Zones (VSZs), starting with the Moyar River Valley in the Nilgiris Biosphere Reserve. This initiative aims to protect vultures from harmful veterinary drugs like diclofenac, which has contributed to their rapid decline.
Key Points
What are Vultures?
Types of Vultures in India
1. Indian Vulture (Gyps indicus)
o IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
o Features: Medium-sized, pale body with dark wings, nests on cliffs and trees. Primarily feeds on livestock carcasses.
o Threats: Poisoning from veterinary drugs like diclofenac.
2. Slender-billed Vulture (Gyps tenuirostris)
o IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
o Features: Thin bill, narrow neck, prefers forested river valleys, and grasslands. Highly sensitive to NSAID poisoning.
3. White-rumped Vulture (Gyps bengalensis)
o IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
o Features: Dark body with a white rump patch, common near villages and slaughterhouses, heavily impacted by diclofenac poisoning.
4. Red-headed Vulture (Sarcogyps calvus)
o IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
o Features: Bare red head, black body, solitary nature, feeds on large carcasses in forests and scrublands.
5. Egyptian Vulture (Neophron percnopterus)
o IUCN Status: Endangered
o Features: Small with yellow face, white-black plumage, often found near human settlements, feeds on carrion and garbage.
6. Griffon Vulture (Gyps fulvus)
o IUCN Status: Least Concern
o Features: Large pale-brown vulture with white neck ruff, common in north-western India, adapted to open and rocky habitats.
7. Himalayan Vulture (Gyps himalayensis)
o IUCN Status: Near Threatened
o Features: Very large with pale plumage, inhabits high-altitude Himalayan cliffs, dominant scavenger in mountain ecosystems.
8. Cinereous Vulture (Aegypius monachus)
o IUCN Status: Near Threatened
o Features: One of the heaviest vultures, dark brown-black body, massive beak, feeds on large carcasses.
9. Bearded Vulture (Gypaetus barbatus)
o IUCN Status: Near Threatened
o Features: Long tail, feathered face, red eye rings, feeds mainly on bones, found in rocky Himalayan terrain.
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding Vultures in India:
1. The IUCN status of the Indian Vulture is Critically Endangered.
2. The Bearded Vulture is found in the rocky terrain of the Himalayan region and feeds mainly on bones.
3. All species of vultures in India are listed as either Least Concern or Near Threatened.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
• Statement 1 is correct: The Indian Vulture is indeed Critically Endangered according to the IUCN Red List.
• Statement 2 is correct: The Bearded Vulture is found in the Himalayan rocky terrains and feeds primarily on bones.
• Statement 3 is incorrect: The Egyptian Vulture is listed as Endangered, and several other species are Critically Endangered.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS 2: Social Justice – Government Policies and Interventions for Development in Various Sectors
Context:
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana–National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) has launched a National Campaign on Entrepreneurship to scale up non-farm livelihood opportunities for rural women. This initiative aims to transform rural incomes and work towards the government’s goal of creating three crore Lakhpati Didis across India.
Key Points
Focus on Non-Farm Rural Livelihoods
Role of Community Resource Persons (CRPs)
Launch of the National Campaign on Entrepreneurship
Scale, Targets, and Expected Impact
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana–National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM):
1. DAY-NRLM exclusively promotes agricultural livelihoods for rural women.
2. The Lakhpati Didi initiative aims for SHG women to earn ₹1 lakh annually.
3. The DAY-NRLM campaign focuses only on providing credit facilities to rural women.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus: GS 2: Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations
Context:
The Responsible Nations Index (RNI) is set to be launched on January 19, 2026, by the World Intellectual Foundation. This initiative aims to assess how countries perform across key dimensions of responsibility in domestic governance, environmental stewardship, and international engagement. The launch highlights the growing global focus on ethical governance, sustainability, and cooperative global behaviour.
Key Points
Institutions and Launch Details
Vision Behind the Index
Three Core Dimensions of Assessment
1. Internal Responsibility
o Focuses on dignity, justice, and the overall well-being of citizens.
2. Environmental Responsibility
o Evaluates stewardship of natural resources and climate action efforts.
3. External Responsibility
o Assesses peace, international cooperation, and a nation’s contribution to global stability.
These dimensions aim to present a holistic picture of responsible nationhood.
Coverage and Methodological Approach
UPSC Prelims Practice Question
Consider the following statements about the Responsible Nations Index (RNI):
1. The RNI will assess the internal, environmental, and external responsibility of nations.
2. It only covers economic performance and does not focus on social or environmental dimensions.
3. The RNI is based on data sourced solely from government reports.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 only
Explanation:
Source: The Hindu